Lodgepole Pine Tree Information
Images of Lodgepole Pine:

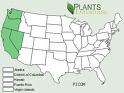


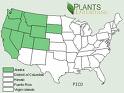

Lodgepole Pine grows in the following 7 states and provinces:
California, Colorado, Hawaii, Maine, Nevada, Oregon, WashingtonInformation about Lodgepole Pine:
The Pinus Contorta Var. Murrayana is commonly known as the Lodgepole Pine, Sierra Lodgepole Pine, Sierra-Cascade Lodgepole Pine as well as Tamarack Pine.
The currently accepted scientific name of Sierra lodgepole pine is Pinus contorta var. murrayana (Grev. & Balf.) Engelm. . Sierra lodgepole pine is one of four recognized varieties of lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta). The other three varieties are listed below : shore pine (Pinus contorta var. contorta), Rocky Mountain lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta var. latifolia) Mendocino White Plains lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta var. bolanderi) This write-up will focus on Sierra lodgepole pine. Sierra lodgepole pine occurs in the Cascade Range of southern Washington, Oregon, and California ; it also occurs in the Sierra Nevada and Klamath Mountains. Disjunct populations occur farther south in the Transverse and Peninsular ranges and the Sierra de Juarez of Baja California . Sierra lodgepole pine is also found in the Virginia and Sweetwater mountains of the Great Basin .Sierra lodgepole pine is a dominant or codominant species in upper montane and subalpine forests . A poorly defined lodgepole pine zone occurs above the red fir (Abies magnifica) zone and below the subalpine forests of mountain hemlock (Tsuga mertensiana), whitebark pine (Pinus albicaulis), and western white pine (P. monticola) . Sierra lodgepole pine forms extensive, pure stands in the Sierran lodgepole pine zone . Sierra lodgepole pine is listed as a dominant or indicator species in the following published classifications: Preliminary plant associations of the southern Oregon Cascade Mountain Province Preliminary plant associations of the Siskiyou Mountain Province Vegetation types of the San Gabriel Mountains Riparian zone associations of Deschutes, Ochoco, Fremont, and Winema National Forests Vegetation types of the San Bernadino Mountains Montane forests of the Sierra Nevada and Cascade Ranges Subalpine forests of the Transverse and Peninsular Ranges Vascular plant communities of California Plant associations of the central Oregon Pumice Zone Some of the information provided here is attributed to:Cope, Amy B. 1993. Pinus contorta var. murrayana. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). , available at the USDA Fire Effects Information System (FEIS) website