Cupressus Goveniana Tree Information
Images of Cupressus Goveniana:




Cupressus Goveniana grows in the following 2 states and provinces:
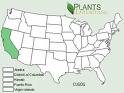
California, HawaiiInformation about Cupressus Goveniana:
as well ashe Cupressus Goveniana is commonly known as the Gowen Cypress.
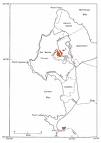
The currently accepted scientific name of Gowen cypress is Cupressus goveniana Gord. (Cupressaceae) . There are two recognized subspecies : C. goveniana ssp. goveniana Gord. Gowen cypress C. goveniana ssp. pygmaea (Lemm.) Bartel Mendocino or pygmy cypress As used in this write-up, "Gowen cypress" refers to both subspecies unless C. goveniana ssp. goveniana is specifically indicated. Mendocino cypress was previously considered a variety of Gowen cypress, but has been given subspecies status by J. Bartel . Santa Cruz cypress (C. abramsiana), listed as a variety of Gowen cypress by Wolf and Little , has since been given species status by Hickman .Gowen cypress is restricted to the Coast Ranges of central and northwestern California . Gowen cypress (Cupressus goveniana ssp. goveniana) occurs in only two areas of Monterey County, California: Huckleberry Hill, and between San Jose Creek and Gibson Creek . Mendocino cypress occurs in a narrow, discontinuous strip along the Mendocino County coast known as the "Mendocino White Plains" or "pine barrens" . A grove also occurs in Sonoma County . Gowen cypress is cultivated in Hawaii . Gowen cypress can occur in dense thickets as well as in open groves. Dense thickets are common in regenerating burns . In Monterey County, Gowen cypress (Cupressus goveniana ssp. goveniana) and bishop pine (P. muricata) form almost impenetrable thickets . In some areas Gowen cypress is associated with closed-cone coniferous woodlands and closed-cone pine-cypress forests . Mendocino cypress is associated with redwood (Sequoia sempervirens)-Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) and other north coast coniferous forests in Mendocino County . This subspecies is also a component of the Mendocino pygmy cypress forest, which intergrades with upland redwood and Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis)-grand fir (Abies grandis) forests . Gowen cypress (C. g. ssp. goveniana) is a component of the Monterey pygmy cypress forest, which intergrades with Monterey pine (Pinus radiata) forest on deep soils . Publications naming Gowen cypress as a community dominant are listed below. Preliminary descriptions of the terrestrial natural communities of California The vascular plant communities of California The closed-cone pines and cypress Species not previously mentioned but commonly associated with Gowen cypress include Monterey cypress (Cupressus macrocarpa), Mendocino White Plains lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta ssp. bolanderi), shore pine (P. c. ssp. contorta), valley oak (Quercus lobata), Coulter willow (Salix coulteri), Monterey ceanothus (Ceanothus rigidus), glory brush (C. gloriosus var. exaltatus), waveyleaf ceanothus (C. foliosus), sandmat manzanita (Arctostaphylos pumila), Hooker manzanita (A. hookeri), hairy manzanita (A. columbiana), glossyleaf manzanita (A. nummularia), Eastwood manzanita (A. glandulosa), Pacific bayberry (Myrica californica), giant chinquapin (Chrysolepis chrysophylla), salal (Gaultheria shallon), Eastwood's goldenbush (Enceliopsis fasciculata), chamise (Adenostoma fasciculatum), evergreen huckleberry (Vaccinium ovatum), Pacific rhododendron (Rhododendron macrophyllum), coast Labrador tea (Ledum glandulosum var. columbianum), navarretia (Navarretia atractyloides), skunkweed (N. squarrosa), bush monkeyflower (Mimulus aurantiacus), evergreen violet (Viola sempervirens), pink sand verbena (Abronia umbellata), Monterey sedge (Carex montereyensis), California canarygrass (Phalaris californica), and beargrass (Xerophyllum tenax) .Some of the information provided here is attributed to:Esser, Lora L. 1994. Cupressus goveniana. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). , available at the USDA Fire Effects Information System (FEIS) website